Search Tips and Hints for Point-in-Time
There are five main ways of searching in the Point-in-Time Services.
1. Quick Search
Located in the top right hand corner under the "Log Off"button, the Quick Search enables you to search by keyword or phrase across all content in the Point-in-Time Service.
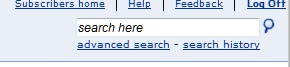
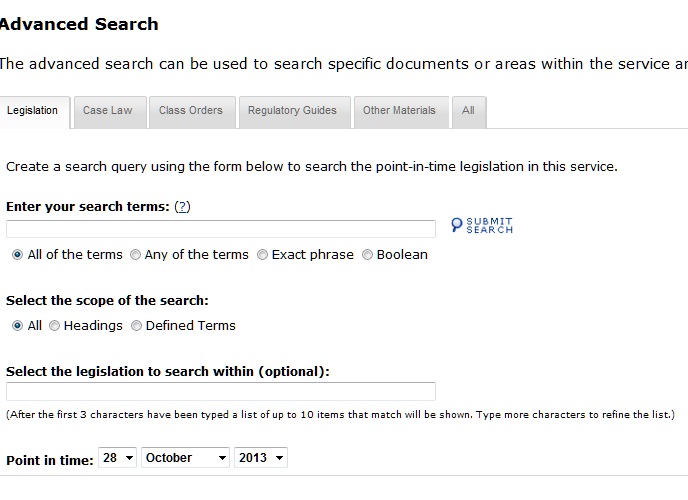
2. Legislation Search - Advanced Search
This Advanced Search is located in the first tab of the Advanced Search link, located under the Quick Search (seen in the picture above).
All search terms are defined by the common Boolean Operators, as detailed in Point 6 below, and also by predictive text to locate a specific piece of legislation. You can also narrow a legislation search to use either headings or defined terms as well.
Unique to Point-in-Time, you can also define a particular date at which you would like the search to be conducted.
3. Case Law Search - Advanced Search
This Advanced Search is located in the second tab of the Advanced Search link, located under the Quick Search (seen in the picture in Point 1 above).
All search terms are defined by the common Boolean Operators, as detailed in Point 6 below, and also by predictive text to locate a specific case to search within. You can also narrow a case law search to use either case name, citations (which do not need to have the correct brackets surrounding the letters and numbers) or catchwords as well.
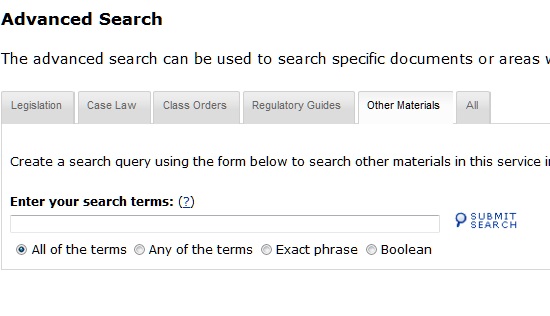
4. Other Materials - Advanced Search
This Advanced Search is located in the third or following tabs of the Advanced Search link, located under the Quick Search (seen in the picture in Point 1 above).
All search terms are defined by the common Boolean Operators, as detailed in Point 6 below, and, depending on the Point-in-Time service selected, there may also be specific searches based on common other materials. for example, ASIC Class Orders in the Corporations Point-in-Time Service.
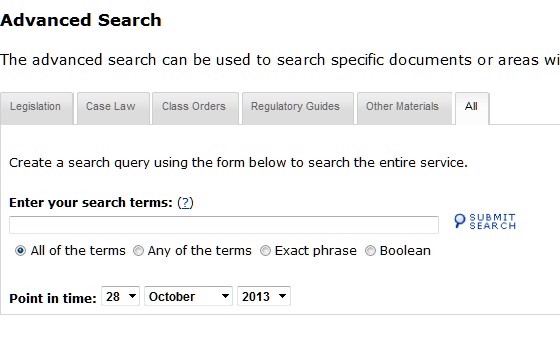
5. Search All - Advanced Search
This Advanced Search is always located in the final tab on the right hand side of the Advanced Search link, located under the Quick Search (seen in the picture in Point 1 above).
All search terms are defined by the common Boolean Operators, as detailed in Point 6 below. Unique to Point-in-Time, you can also define a particular date at which you would like the search to be conducted.
6. Common Search Operators - All Advanced Search Templates
There are four common search operators appearing on all Point-in-Time templates:
- All terms means every term anywhere it appears in the current document
- Any terms means the three words anywhere within 20-30 words of each other
- An exact phrase means to search for that term in that combination alone
- Boolean Search means using your usual Boolean operators which are also included in the Search help
The Common Boolean Operators include the following:
Keyword searches
A keyword search finds all records which contain the words you specify. Separate key words by spaces.
Phrase searches
A phrase search finds all records which contain the exact phrase. The phrase must be enclosed in quotes.
Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT)
Boolean operators require a word or phrase on either side of the operator. For example, dog or cat is a valid query, but or cat is not.
Operator Precedence
The search operators have a precedence order. That is, when two more operators are used in a search, the results of one operator will be evaluated before another operator. Understanding the precedence — and how to override the precedence — can assist you in finding the information you need.
The operator precedence is: Not, Or, And
If the same operators are used in a query, the operators are evaluated from left-to-right.
Truncation operator (*)
The truncation operator allows you to find words using patterns for a set of words replacing single or multiple characters. The truncation operator cannot be used in exact phrase searches.
No proximity operators are available.
If you haven't found what you are looking for or would like more information, please see our Frequently Asked Questions.
